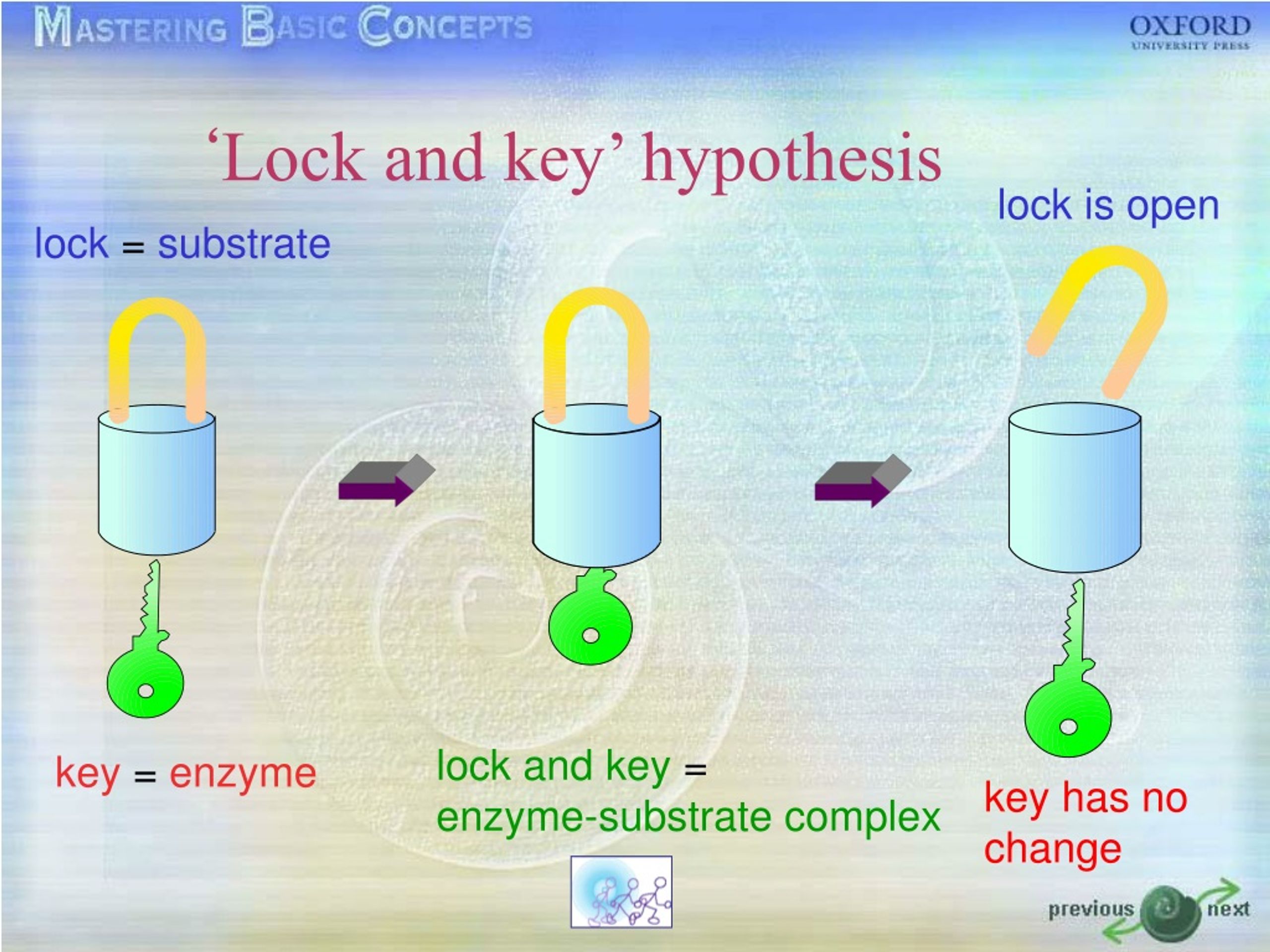
Explain Lock Hypothesis . This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates.
from www.slideserve.com
in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific.
PPT Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9144369
Explain Lock Hypothesis In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish.
From www.youtube.com
Lock 6 2 Hypothesis test for mean YouTube Explain Lock Hypothesis the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
Lock and Key Model of Enzyme YouTube Explain Lock Hypothesis the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. in the lock and. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.biologybrain.com
Mechanism of Enzyme Action (Activation Energy and Lock and Key Explain Lock Hypothesis In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2058626 Explain Lock Hypothesis the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From telgurus.co.uk
Explain the Lock and key mechanism in relation to enzymes. Science Explain Lock Hypothesis This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific.. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.slideshare.net
Lock and Key Hypothesis A New Perspective Explain Lock Hypothesis the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
Lock and Key Hypothesis YouTube Explain Lock Hypothesis in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From guides.hostos.cuny.edu
Chapter 9 Proteins and Enzymes CHE 120 Introduction to Organic Explain Lock Hypothesis In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
How enzymes work catalase & the lock and key hypothesis YouTube Explain Lock Hypothesis In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. This model portrayed the. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 5 Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Explain Lock Hypothesis In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. This model portrayed the. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
Lock 6 5 Hypothesis Test for Matched Pairs NEW YouTube Explain Lock Hypothesis in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. This model portrayed. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.slideshare.net
C26 Digestion In Human Explain Lock Hypothesis In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.biologyonline.com
Induced fit model Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Explain Lock Hypothesis In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
Worst Explanation of Lock and Key Hypothesis (don't watch this if you Explain Lock Hypothesis In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. This model portrayed the. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.researchgate.net
16. A schematic presentation of the allocentric lock hypothesis (Riva Explain Lock Hypothesis in the lock and key model, first presented by emil fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. In this model,. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
Mode of Enzyme actionLock and key hypothesisInduced fit hypothesis Explain Lock Hypothesis In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. in the lock and. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.vecteezy.com
The Lock and Key Mechanism of enzyme action on substrate 20240683 Explain Lock Hypothesis the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer, is a fundamental concept in biochemistry that explains enzyme specificity. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to in. Explain Lock Hypothesis.
From www.studocu.com
Theories of enzyme catalysis1 THE FISCHER 'LOCKANDKEY' HYPOTHESIS Explain Lock Hypothesis the lock and key model is a hypothesis explaining how enzymes interact with substrates. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to In 1894, emil fisher discovered that glycolytic enzymes are able to distinguish. In this model, enzymes are depicted as highly specific. the lock and key theory, introduced by emil fischer,. Explain Lock Hypothesis.